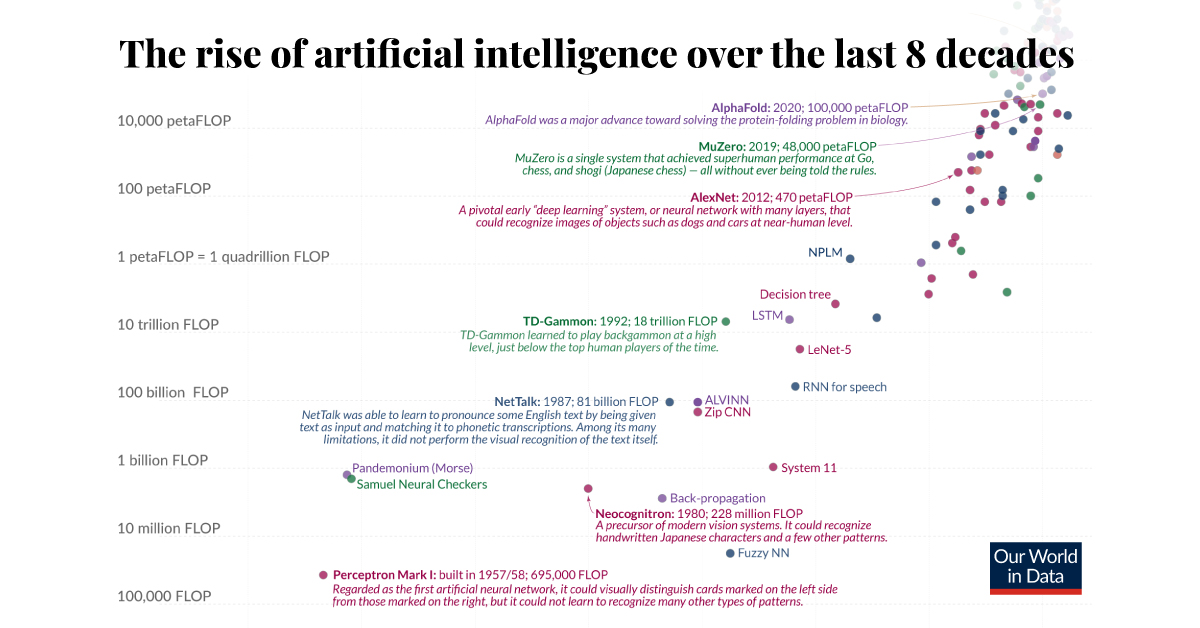
### Summary
Artificial intelligence (AI) has made significant advancements since its inception in the 1950s, with developments such as neural networks, chatbots, deep learning, and machine translation. AI has had a transformative impact on various industries and continues to evolve, with ongoing research and new applications being developed.
### Facts
- 🤖 AI is the ability of computers to perform tasks that typically require human cognition, and it has gained widespread attention in recent years.
- 🌍 AI has infiltrated various aspects of our lives, from healthcare advancements to business operations.
- 🔑 AI is considered to be big data's great equalizer, as it can collect, analyze, democratize, and monetize information more efficiently.
- 📅 The timeline of AI development includes key milestones such as the introduction of neural networks and the coining of terms like artificial intelligence and machine learning in the 1950s.
- 🚀 Notable developments in AI include the creation of chatbots, intelligent robots, deep learning algorithms, facial recognition systems, and self-driving cars.
- 🌐 AI has also faced challenges, including periods of AI winter, funding issues, and concerns over the impact of AI on society.
### Key Developments:
- 🗓️ 1950: Alan Turing introduced the Turing test and laid the foundation for AI research.
- 🗓️ 1960s: Eliza, the first chatbot, and Shakey, the first mobile intelligent robot, were developed.
- 🗓️ 1980s: The term "AI winter" was coined, symbolizing a decline in AI research.
- 🗓️ 2000s: IBM's Watson, personal assistants, facial recognition systems, deepfakes, and autonomous vehicles emerged.
- 🗓️ 2020s: OpenAI released GPT-3 and AlphaFold, Google introduced transformers, and Microsoft launched Turing NLG.
### Future Outlook:
- 🌟 The future of AI is promising, with potential applications in various industries, including healthcare, finance, marketing, and transportation.
- 🔬 Ongoing advancements in neuromorphic processing and artificial general intelligence aim to mimic human brain cells and achieve more complex cognitive abilities.
- 🤝 Ethical considerations, transparency, privacy, and trust will continue to be important as AI evolves and impacts society and business processes.
The rapid growth of AI, particularly generative AI like chatbots, could significantly increase the carbon footprint of the internet and pose a threat to the planet's emissions targets, as these AI models require substantial computing power and electricity usage.
The transformation of data servers to be AI-ready is consuming significant energy and natural resources, raising the question of whether AI can revolutionize technology's carbon footprint responsibly.
The rise of artificial intelligence (AI) is a hot trend in 2023, with the potential to add trillions to the global economy by 2030, and billionaire investors are buying into AI stocks like Nvidia, Meta Platforms, Okta, and Microsoft.
Google CEO Sundar Pichai believes that AI will be the biggest technological shift of our lifetimes and may be even bigger than the internet itself, as Google focuses more on AI after the rise of generative AI threatened its core business.
The global AI market is projected to reach $2 trillion by 2030, with companies like Amazon and Meta Platforms making significant investments in AI to drive growth and diversify their offerings.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is poised to be the biggest technological shift of our lifetimes, and companies like Nvidia, Amazon, Alphabet, Microsoft, and Tesla are well-positioned to capitalize on this AI revolution.
Artificial intelligence (AI) is predicted to be a major growth driver during the upcoming bull market, with AI software sales expected to reach $1.1 trillion by 2032; two AI growth stocks to consider are HubSpot, which offers AI sales assistant software and plans to release new AI products, and Arista Networks, which provides high-speed networking equipment and software for cloud and enterprise data centers.
Salesforce announced new AI initiatives at its Dreamforce conference, but analysts predict that it will take until 2024/2025 for these AI solutions to drive significant revenue growth for the company.
Artificial intelligence (AI) will continue to evolve and become more integrated into our lives in 2024, with advancements in generative AI tools, ethical considerations, customer service, augmented working, AI-augmented apps, low-code/no-code software engineering, new AI job opportunities, quantum AI, upskilling for the AI revolution, and AI legislation.
Microsoft's AI monetization opportunity is expected to show strong growth as the adoption curve for AI in the cloud is happening quicker than expected, with the potential for significant revenue from AI functionality like Microsoft CoPilot, according to Wedbush analyst Dan Ives.
Artificial intelligence's rapid growth and adoption is leading to a significant increase in energy consumption, particularly in data centers, raising concerns about the environmental impact and the need for more efficient energy solutions.
Advancements in AI have continued to accelerate despite calls for a pause, with major players like Amazon, Elon Musk, and Meta investing heavily in AI startups and models, while other developments include AI integration into home assistants, calls for regulation, AI-generated content, and the use of AI in tax audits and political deepfakes.
Artificial intelligence is predicted to have a significant economic impact of nearly $16 trillion by 2030, with the potential to disrupt every sector and boost revenue through the integration of generative AI tools.
The adoption of large language models (LLMs) and generative AI is raising concerns about the surge in datacenter electricity consumption, as the inference phase of AI models is often overlooked and could contribute significantly to energy costs. Estimates show that AI-powered search capabilities in Google could consume as much electricity as a country like Ireland per year. While improvements in efficiency may limit the growth of AI-related electricity consumption in the near term, long-term changes and the indiscriminate use of AI should be questioned.
A new study warns that the widespread adoption of artificial intelligence technology could lead to a substantial increase in electricity consumption, with AI systems relying on powerful servers and potentially driving a spike in energy demand.
The global AI industry could consume as much as 134 TWh of electricity annually by 2027, which is comparable to the annual consumption of countries like Argentina and the Netherlands, according to expert analysis. As AI becomes more prevalent, its energy needs will continue to grow, highlighting the importance of carefully considering where and when to use AI technologies.
The growth of artificial intelligence could significantly increase energy consumption, with AI servers potentially using as much electricity as small countries do in a year, according to an analysis published in Joule. The study highlights the need for sustainability considerations in AI development and calls for greater transparency and data on energy use in the industry.
India's Ministry of Electronics and Information Technology (MeitY) has published an AI vision document proposing the development of a national computing infrastructure with 80 exaFLOPS of power across three layers and a distributed data grid. The infrastructure will include high-end compute, an inference arm, and edge compute, and aims to enhance AI capabilities in the country. However, the planned investment falls short of China's recent announcement of 150 exaFLOPS of additional power and 1,800 exabytes of national storage capacity.
Spending on generative AI solutions, which includes software, hardware, and IT/business services, is predicted to reach $143 billion by 2027, with enterprises investing nearly $16 billion in 2023 alone, according to a new report by International Data Corporation (IDC). This represents a compound annual growth rate of 73.3% over the 2023-2027 forecast period and demonstrates that generative AI is becoming a transformative technology with significant business impact.
Artificial intelligence is becoming a key driver of revenue for businesses, particularly in the Middle East, as companies invest heavily in data collection and capitalizing on it, with the potential for the region to benefit from a $320 billion economic impact by 2030.