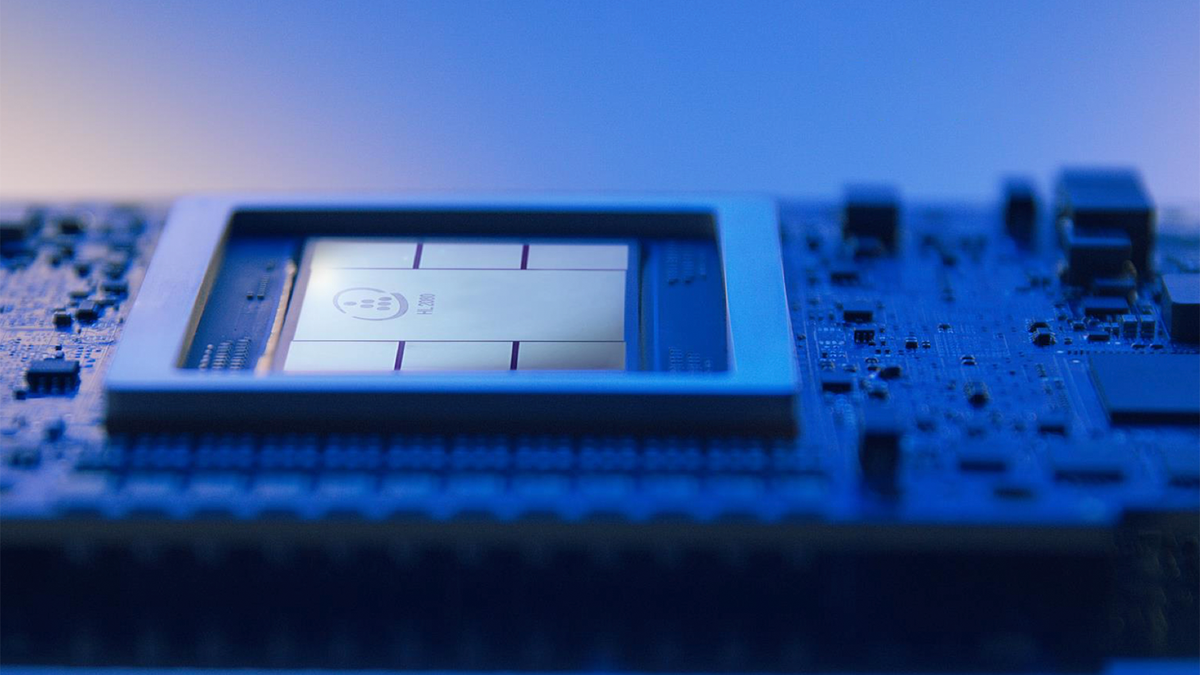
Nvidia has announced the second generation GH200 superchip, which combines the Grace CPU and the Hopper GPU, offering increased memory capacity and bandwidth for AI training and inference workloads. The upgraded superchip uses HBM3e memory, enabling a 76.3% increase in memory capacity and a 49.3% increase in memory bandwidth compared to the original Hopper SXM5 device.
Nvidia has reported explosive sales growth for AI GPU chips, which has significant implications for Advanced Micro Devices as they prepare to release a competing chip in Q4. Analysts believe that AMD's growth targets for AI GPU chips are too low and that they have the potential to capture a meaningful market share from Nvidia.
Nvidia's impressive earnings growth driven by high demand for its GPU chips in AI workloads raises the question of whether the company will face similar challenges as Zoom, but with the continuous growth in data center demand and the focus on accelerated computing and generative AI, Nvidia could potentially sustain its growth in the long term.
Nvidia, the world's most valuable semiconductor company, is experiencing a new computing era driven by accelerated computing and generative AI, leading to significant revenue growth and a potential path to becoming the largest semiconductor business by revenue, surpassing $50 billion in annual revenue this year.
Bill Dally, NVIDIA's chief scientist, discussed the dramatic gains in hardware performance that have fueled generative AI and outlined future speedup techniques that will drive machine learning to new heights. These advancements include efficient arithmetic approaches, tailored hardware for AI tasks, and designing hardware and software together to optimize energy consumption. Additionally, NVIDIA's BlueField DPUs and Spectrum networking switches provide flexible resource allocation for dynamic workloads and cybersecurity defense. The talk also covered the performance of the NVIDIA Grace CPU Superchip, which offers significant throughput gains and power savings compared to x86 servers.
Nvidia has been a major beneficiary of the growing demand for artificial intelligence (AI) chips, with its stock up over 3x this year, but Advanced Micro Devices (AMD) is also poised to emerge as a key player in the AI silicon space with its new MI300X chip, which is targeted specifically at large language model training and inference for generative AI workloads, and could compete favorably with Nvidia.
Nvidia predicts a $600 billion AI market opportunity driven by accelerated computing, with $300 billion in chips and systems, $150 billion in generative AI software, and $150 billion in omniverse enterprise software.
The video discusses Nvidia, Intel, and Advanced Micro Devices in relation to the current AI craze, questioning whether the current leader in the field will maintain its position.
Semiconductor stocks, particularly Nvidia, have outperformed the market due to the high demand for chips in AI applications, making Nvidia the better AI stock to buy compared to Intel.
Nvidia's success in the AI industry can be attributed to their graphical processing units (GPUs), which have become crucial tools for AI development, as they possess the ability to perform parallel processing and complex mathematical operations at a rapid pace. However, the long-term market for AI remains uncertain, and Nvidia's dominance may not be guaranteed indefinitely.
Despite a decline in overall revenue, Dell Technologies has exceeded expectations due to strong performance in its AI server business, driven by new generative AI services powered by Nvidia GPUs, making it a potentially attractive investment in the AI server space.
Nvidia and Intel emerged as the top performers in new AI benchmark tests, with Nvidia's chip leading in performance for running AI models.
Nvidia's strong demand for chips in the AI industry is driving its outstanding financial performance, and Micron Technology could benefit as a key player in the memory market catering to the growing demand for powerful memory chips in AI-driven applications.
Large language models like Llama2 and ChatGPT perform well on datacenter-class computers, with the best being able to summarize more than 100 articles in a second, according to the latest MLPerf benchmark results. Nvidia continues to dominate in performance, though Intel's Habana Gaudi2 and Qualcomm's Cloud AI 100 chips also showed strong results in power consumption benchmarks. Nvidia's Grace Hopper superchip, combined with an H100 GPU, outperformed other systems in various categories, with its memory access and additional memory capacity contributing to its advantage. Nvidia also announced a software library, TensorRT-LLM, which doubles the H100's performance on GPT-J. Intel's Habana Gaudi2 accelerator is closing in on Nvidia's H100, while Intel's CPUs showed lower performance but could still deliver summaries at a decent speed. Only Qualcomm and Nvidia chips were measured for datacenter efficiency, with both performing well in this category.
Intel CEO Pat Gelsinger emphasized the concept of running large language models and machine learning workloads locally and securely on users' own PCs during his keynote speech at Intel's Innovation conference, highlighting the potential of the "AI PC generation" and the importance of killer apps for its success. Intel also showcased AI-enhanced apps running on its processors and announced the integration of neural-processing engine (NPU) functionality in its upcoming microprocessors. Additionally, Intel revealed Project Strata, which aims to facilitate the deployment of AI workloads at the edge, including support for Arm processors. Despite the focus on inference, Intel still plans to compete with Nvidia in AI training, with the unveiling of a new AI supercomputer in Europe that leverages Xeon processors and Gaudi2 AI accelerators.