Main Topic: U.S. gas prices hit an eight-month high amid rising oil prices.
Key Points:
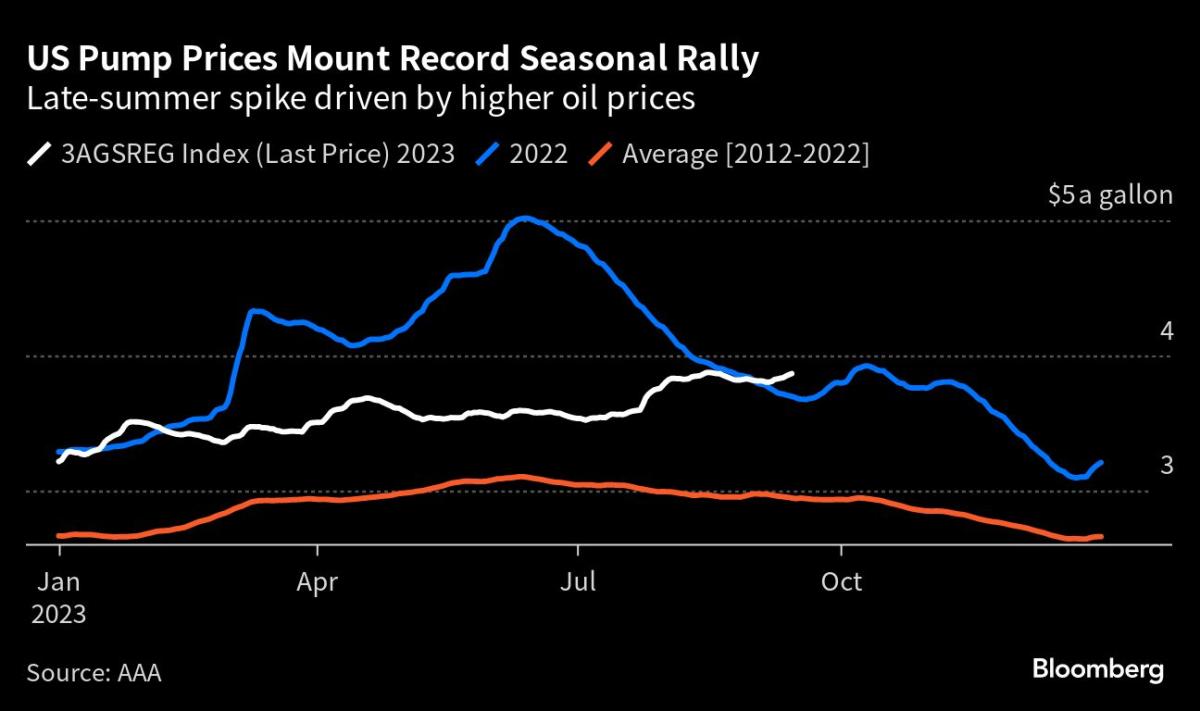
1. National average price for a gallon of regular unleaded climbed to $3.71, the highest level since November.
2. Gas prices are up by at least $0.15 cents in 16 states in the past week alone.
3. Surge in oil prices, production cuts by OPEC nations, and U.S. refinery outages contribute to the increase in gas prices.
The surge in gasoline prices poses risks for President Joe Biden and his green agenda, despite the fact that U.S. oil production is on track to set a new record this year and is expected to continue rising in the future.
Rising gasoline prices are impacting inflation-weary Americans.
Gas prices in the US are nearing $4 a gallon, up 60 cents since the start of the year, which could complicate the Federal Reserve's decision on interest rates as it tries to rein in inflation.
Diesel prices in the US have reached their highest levels since March and are expected to continue rising due to refinery disruptions and increased demand during the fall agricultural harvest season and winter heating months, posing challenges for retailers and putting upward pressure on prices.
The average retail price of regular gasoline in the United States has increased by 6% over the past five weeks, reaching $3.81 per gallon heading into the Labor Day weekend, due to factors such as oil production cuts, low gasoline inventories, and refinery maintenance.
Gas prices are historically high for Labor Day, with the national average for regular gas at $3.83 a gallon and some states averaging $4 a gallon or more due to factors such as OPEC holding back supply, extreme heat affecting refineries, and easing recession fears boosting oil prices.
Crude oil prices reached their highest level of the year after Saudi Arabia and Russia agreed to cut output, raising concerns about gasoline prices for American consumers.
The price of crude oil may reach triple digits by the end of next year, potentially impacting Americans' voting decisions, as global demand for oil is projected to reach a record high of 102 million barrels per day, according to the International Energy Agency and Goldman Sachs analysts.
Crude oil prices in the US increased due to a 6.3 million barrel inventory draw, following a massive decline of 10.6 million barrels the previous week, bringing inventories to the lowest in eight months.
Oil prices reach new highs in 2023 due to supply constraints caused by output reductions from Saudi Arabia and Russia, raising concerns about global inventory shortages and potential inflationary pressures.
Gasoline prices contributed to a rise in inflation in August, but economists believe that the increase is temporary and that overall inflation is headed towards normal levels.
President Joe Biden has promised to lower U.S. gasoline prices, addressing voter frustration over the economy as consumer inflation rises.
Oil prices reached their highest level of the year, with analysts predicting that prices could reach $100 a barrel by the end of the year due to tighter supply and production constraints from Saudi Arabia and Russia.
Gas prices in the United States have been increasing due to OPEC's reduction in drilling, and California has the highest gas prices in the country due to high state taxes and limited competition in the gasoline market.
Gasoline prices are rising due to oil supply cuts in Saudi Arabia and Russia, as well as flooding in Libya, but some experts believe that increasing oil prices will not have a significant impact on the US economy and do not expect them to rise much higher in the next year or two due to factors such as increased US oil production, slow global economic growth, and the green energy transition. However, high oil prices can lead to higher inflation, potential recession, and could influence the Federal Reserve to raise interest rates, but the impact may not be as severe as in the past, and some experts recommend investing in the energy transition and adopting a more defensive investment strategy.
Gas prices in Los Angeles County have climbed rapidly, with the average price per gallon increasing by nearly 20 cents in just 48 hours due to ongoing refinery issues and unexpected outages.
The average price of gasoline in the United States has risen to $3.881 per gallon, compared to $3.678 per gallon a year ago, due to refinery outages in the western United States.
Crude oil prices reach new highs despite concerns about China's economy and tightened monetary policies, with the oil market structure indicating strong demand and potential support for higher prices.
Oil prices reach a 3-month high as OPEC maintains tight supply. Gas prices in the US rise, posing a threat to efforts against inflation.
Gas prices are expected to rise to $100 per barrel of crude oil, but experts believe consumers will be able to handle the increase, with some price easing predicted in the future.
Oil prices are rising again after a short pause, driven by Russia's temporary ban on fuel exports and concerns of low supply, with analysts predicting it could hit $100 a barrel for the first time in 13 months.
Gas prices in the United States have risen, exceeding the highs of last year, with California having the highest prices due to high state taxes and issues at refineries, as well as a less competitive gasoline market caused by certain refineries controlling a large portion of the market.
Oil prices hit their highest levels in over a year as ongoing production cuts raise concerns about the global economy, while the specter of $100 oil looms and supply tightness becomes apparent with reduced stockpiles and increased refining. Higher interest rates may dampen crude demand, but for now, the focus remains on supply.
Gasoline prices have increased over time, but when adjusted for inflation and considered in relation to fuel efficiency and real wages, they are only marginally more expensive than in previous years, highlighting the often misleading nature of political rhetoric surrounding gas prices.
United States domestic oil production reached a record high, contradicting efforts to reduce carbon emissions, leading to concerns about undermining global efforts to reduce emissions and combat climate change.