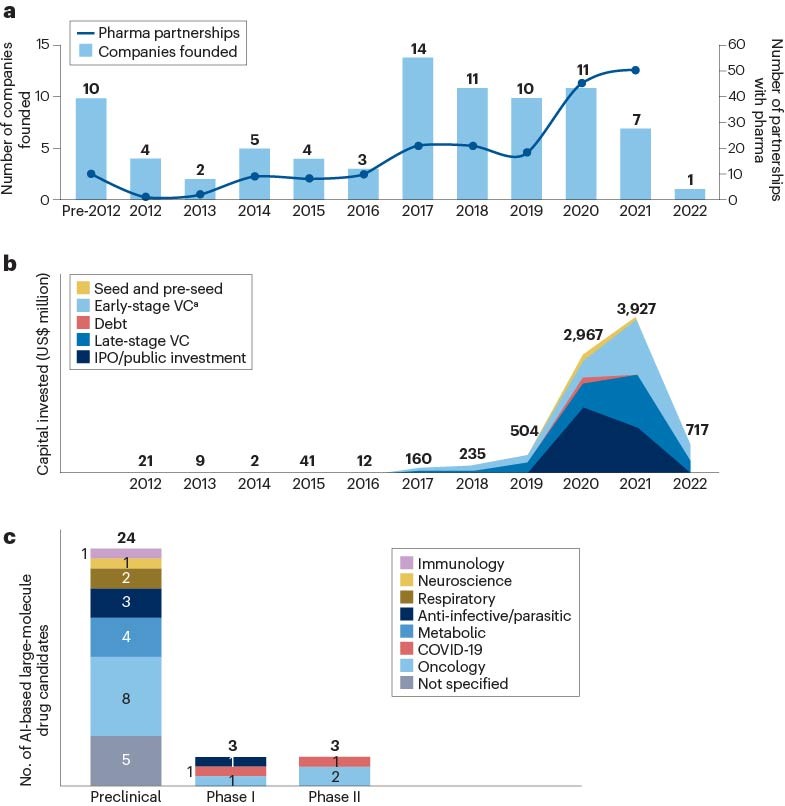
The global market for artificial intelligence (AI) in drug discovery is projected to grow significantly in the coming years, with emerging companies adding value and the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases driving demand, although limitations and a shortage of AI workforce may hinder growth.
Scientists have used AI to design proteins with two different states, essentially creating biological transistors that can change their shape depending on inputs, opening up new possibilities for biotechnology and medical solutions.
Chemists are developing a chemical map of all possible molecules to accelerate the discovery process for drugs and materials, with the help of artificial intelligence to determine the properties and viability of these molecules.
Precision oncology is a revolution in cancer care that matches the right treatments to patients, and applying artificial intelligence and machine learning to clinical, genomic, and social determinants of health data can help develop targeted prevention strategies and new treatments while identifying eligible patients.
AI-assisted drug discovery has led to the discovery of a new antibiotic called halicin, which has the potential to kill antibiotic-resistant bacteria, marking a significant breakthrough in addressing the public health issue of superbugs; the use of AI has expedited the drug discovery process by analyzing vast amounts of medical data and predicting the properties of molecules.
UK-based biotech startup Etcembly has used generative AI to develop a novel immunotherapy for hard-to-treat cancers, demonstrating the potential of AI in speeding up medical advancements; however, a study published in JAMA Oncology highlights the risks of relying solely on AI recommendations in clinical settings, as AI chatbots can contain factual errors and contradictory information in their treatment plans, emphasizing the importance of rigorous validation.
Penn State College of Medicine has awarded $225,000 in pilot funding to researchers as part of its strategic plan to apply artificial intelligence and informatics to advance biomedical research and address health challenges. Nine investigators received seed funding for projects that aim to use cutting-edge technology and computational innovation to develop new therapeutics, diagnostics, and preventive strategies.
The global artificial intelligence in genomics market is projected to reach USD 12.5 billion by 2032, with a CAGR of 39.2% during the period 2023-2032, driven by the increasing adoption of AI in genomics research for analysis and personalized medicine.
The budget for artificial intelligence and machine learning in the healthcare sector is expected to reach 10.5% in 2024, up from 5.5% in 2022, and could have transformational effects on the industry beyond drug discovery, according to Morgan Stanley. Private equity firm Thoma Bravo is also in talks to acquire NextGen Healthcare, while Nestle-partnered weight loss capsules have succeeded in a pivotal trial, boosting shares of Epitomee Medical.
An AI-generated COVID drug enters clinical trials, GM and Google strengthen their AI partnership, and Israel unveils an advanced AI-powered surveillance plane, among other AI technology advancements.
Noetik, an AI drug discovery company, has raised $14 million in seed funding to support its development of precision therapeutics in immuno-oncology using machine learning and human data. The funding will be used to expand Noetik's team and continue the development of transformer-based machine learning methods.
The pharmaceutical market is expected to grow significantly by 2030, reaching $3,206 billion, driven by advances in healthcare technologies, increasing healthcare expenditures, and the rise of chronic diseases. The Business Research Company offers comprehensive reports to assist pharmaceutical companies with informed decision-making and staying competitive in this dynamic sector.
Machine-learning algorithms developed at the University of Michigan can identify problem areas in antibodies that cause them to bind with non-target molecules, enabling researchers to modify the antibodies and optimize their effectiveness in fighting diseases like Parkinson's, Alzheimer's, and colorectal cancer.
Healthcare revenue cycle management provider Aspirion has acquired Artificial Intelligence (AI) and machine learning firm Infinia ML to enhance operational effectiveness, recovery yield, and collections for its healthcare clients. Infinia ML will operate as Aspirion's research and development engine, focusing on AI capabilities to drive financial performance improvements for healthcare providers.
AI is revolutionizing scientific research by accelerating drug discovery, predicting protein structures, improving weather forecasting, controlling nuclear fusion, automating laboratory work, and enhancing data analysis, allowing scientists to explore new frontiers and increase research productivity.
Artificial Intelligence (AI) has the potential to improve healthcare, but the U.S. health sector struggles with implementing innovations like AI; to build trust and accelerate adoption, innovators must change the purpose narrative, carefully implement AI applications, and assure patients and the public that their needs and rights will be protected.
The artificial intelligence (AI) market is rapidly growing, with an expected compound annual growth rate (CAGR) of 37.3% and a projected valuation of $1.81 trillion by the end of the decade, driven by trends such as generative AI and natural language processing (NLP). AI assistants are being utilized to automate and digitize service sectors like legal services and public administration, while Fortune 500 companies are adopting AI to enhance their strategies and operations. The rise of generative AI and the growth of NLP systems are also prominent trends, and AI's use in healthcare is expected to increase significantly in areas such as diagnostics, treatment, and drug discovery.
Professor Brad Pentelute and the Pentelute Lab at MIT are using a combination of chemistry, biology, and engineering to develop new techniques and platforms that have the potential to revolutionize therapeutics, including using nature-inspired research to solve protein delivery problems and building an automated protein printing machine. They are also using machine learning and automation to discover new peptides and proteins that can be used in cancer treatment and other applications, with the goal of rapidly designing molecules with new functions and advancing the field of AI-driven molecule design.
Scientists at The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research have been awarded $3.1 million to develop artificial intelligence and machine learning tools to monitor hospitalized patients and predict deterioration, aiming to improve patient outcomes.
The use of generative AI, combined with federated and active learning, can accelerate the development of protein drugs by improving predictions of drug properties and enabling collaboration among biopharmaceutical companies while protecting their competitive interests.