The U.S. economy is forecasted to be growing rapidly, which is causing concern for the Federal Reserve and those hoping for low interest rates.
A mild recession may benefit the housing market by leading to lower mortgage rates, more available supply, and potentially lower home prices.
Over half of U.S. small business owners believe the economy is already in a recession, though their own financial conditions remain strong and they have less concerns about the health of their banks, according to a survey by the National Federation of Independent Business.
Despite initial predictions of a recession, the U.S. economy has experienced unexpected growth, with high consumer spending and continued borrowing and investment by businesses being key factors.
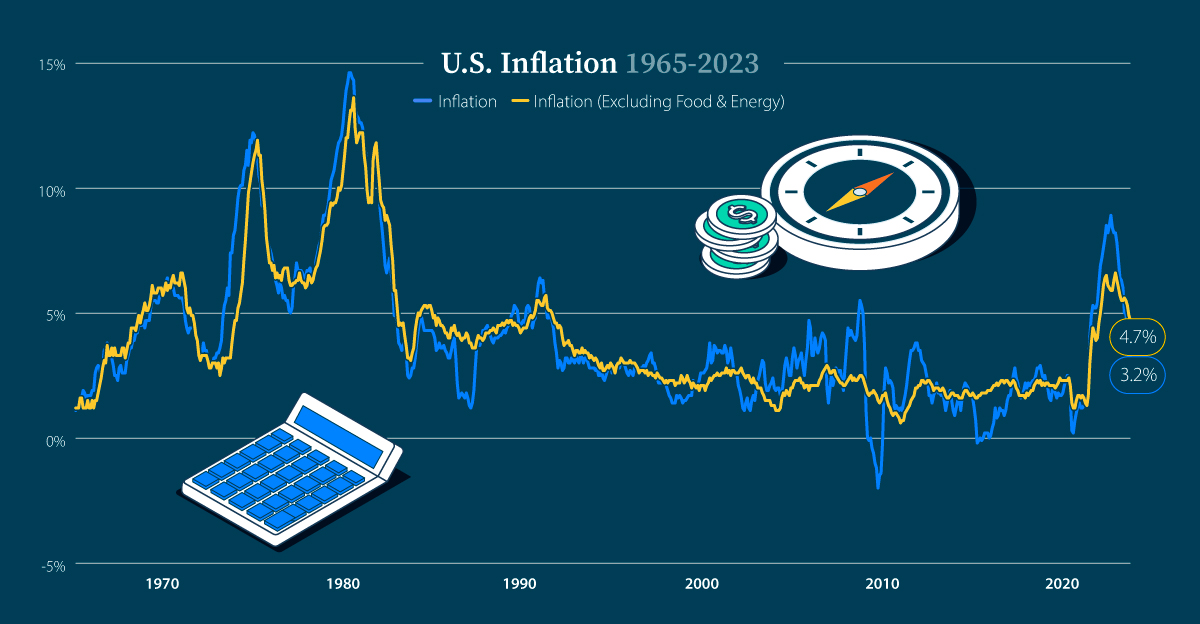
The U.S. economy continues to grow above-trend, consumer spending remains strong, and the labor market is tight; however, there are concerns about inflation and rising interest rates which could impact the economy and consumer balance sheets, leading to a gradual softening of the labor market.
The Federal Reserve faces new questions as the U.S. economy continues to perform well despite high interest rates, prompting economists to believe a "soft landing" is possible, with optimism rising for an acceleration of growth and a more sustainable post-pandemic economy.
The US economy continues to perform well despite the Federal Reserve's interest rate hikes, leading to questions about whether rates need to be higher and more prolonged to cool inflation and slow growth.
Despite the optimism from some economists and Wall Street experts, economist Oren Klachkin believes that elevated interest rates, restrictive Federal Reserve policy, and tight lending standards will lead to a mild recession in late 2023 due to decreased consumer spending and slow hiring, although he acknowledges that the definition of a recession may not be met due to some industries thriving while others struggle.
Fannie Mae economists predict that the U.S. housing market will remain unchanged regardless of whether the economy experiences a soft landing or enters a mild recession, with high mortgage interest rates and housing affordability issues continuing to impact the market. They anticipate that existing home sales will remain subdued, and while a recession may lead to a pullback in construction, a soft landing accompanied by higher mortgage rates could also result in slower housing construction and sales.
Recession fears return as a key business survey shows a significant contraction in the UK economy, signaling the detrimental effects of interest rate rises on businesses and heightening the risk of a renewed economic downturn.
The success of the global economy in the coming months rests heavily on the ability of the US Federal Reserve to achieve a "soft landing" in managing growth-inflation dynamics, as many other major economies are facing their own challenges and cannot serve as alternative engines for global growth.
The US economy is expected to slow in the coming months due to the Federal Reserve's efforts to combat inflation, which could lead to softer consumer spending and a decrease in stock market returns. Additionally, the resumption of student loan payments in October and the American consumer's credit card addiction pose further uncertainties for the economy. Meanwhile, Germany's economy is facing a contraction and a prolonged recession, which is a stark contrast to its past economic outperformance.
The economy is experiencing a soft landing, but the long-term consequences of easy money policies are still uncertain, with bankruptcies and a potential shakeout in office real estate looming.
The U.S. economy grew at a 2.1% annual rate in the second quarter, showing resilience despite higher borrowing costs and a slight downgrade from the initial estimate of 2.4%, driven by consumer spending, business investment, and government outlays.
Morgan Stanley's top economist, Seth Carpenter, believes that the US is nearing a dream economic scenario with falling inflation and steady growth, suggesting that the Federal Reserve is close to achieving a soft landing.
The US economy may face disruption as debts are refinanced at higher interest rates, which could put pressure on both financial institutions and the government, according to Federal Reserve Bank of Atlanta President Raphael Bostic.
The U.S. economy is defying expectations with continued growth, falling inflation, and a strong stock market; however, there is uncertainty about the near-term outlook and it depends on the economy's future course and the actions of the Federal Reserve.
The U.S. economy is heading towards a soft landing, but the actions of Saudi Arabia and Russia may disrupt this trajectory.
Goldman Sachs has lowered its odds of a US recession in the next 12 months to 15% from 20%, citing the resilience of the economy, supportive income growth, and a balanced labor market, with Chief Economist Jan Hatzius suggesting a soft landing is possible and that further rate hikes by the Federal Reserve are unlikely.
Despite recent optimism around the U.S. economy, Deutsche Bank analysts believe that a recession is more likely than a "soft landing" as the Federal Reserve tightens monetary conditions to curb inflation.
U.S. economic growth was modest in July and August, with slowing inflation and a cooling labor market, indicating that the Federal Reserve may be close to finishing its interest rate increases.
The US economy is predicted to enter a recession by spring, leading to a 25% or more crash in the S&P 500, according to economist David Rosenberg, who warns that American consumers are nearing their spending limits and rising home prices reflect a weak housing market.
Australia's economy may not experience a soft landing, according to Treasurer Jim Chalmers, due to potential risks such as China's slowing economy and a slump in household consumption resulting from rising interest rates.
Bank of America warns that the US economy still faces the risk of a "hard landing" due to rising oil prices, a strong dollar, and potential interest rate hikes by the Federal Reserve, contrasting with the optimistic outlook of other Wall Street banks.
Economists predict that inflation will cool without a recession, as the effects of rate hikes have already taken shape, putting the US economy on track for a soft landing.
The odds of a recession in the US have collapsed, making markets vulnerable to any signs of the economy overheating and contributing to inflationary pressures.
The US economy is facing a looming recession, with weakness in certain sectors, but investors should not expect a significant number of interest-rate cuts next year, according to Liz Ann Sonders, the chief investment strategist at Charles Schwab. She points out that leading indicators have severely deteriorated, indicating trouble ahead, and predicts a full-blown recession as the most likely outcome. Despite this, the stock market has been defying rate increases and performing well.
Treasury Secretary Janet Yellen and Goldman Sachs may be optimistic about a "soft landing" scenario for the US economy, but the author remains skeptical due to factors such as a deeply inverted yield curve, declining Leading Economic Indicators, challenges faced by the consumer, global growth concerns, and the lagging impact of the Fed's monetary policy, leading them to maintain a conservative portfolio allocation.
Consumer spending in the US has supported the economy despite concerns of a recession, but rising interest rates, the resumption of student loan payments, and dwindling savings are predicted to put pressure on consumers and potentially lead to a shrinking of personal consumption.
Stronger-than-expected U.S. economic data, including a rise in producer prices and retail sales, has sparked concerns about sticky inflation and has reinforced the belief that the Federal Reserve will keep interest rates higher for longer.
The US economy shows signs of weakness despite pockets of strength, with inflation still above the Fed's 2% target and consumer spending facing challenges ahead, such as the restart of student loan payments and the drain on savings from the pandemic.
Despite economists' hopes for a "soft landing" of the economy, signs such as inflation and uncertain variables make it difficult to determine whether the U.S. economy has achieved this outcome.
Central banks' efforts to combat inflation by raising interest rates have not led to mass job losses, as labor markets in various countries have cooperated by reducing open vacancies and trimming wage growth, suggesting a possible "soft landing" for the economy without significant casualties.
Entrepreneur Jaspreet Singh warns that signs of a potential recession in America include labor shortages, inflation-driven spending, and high interest rates, with economists predicting that the country may start feeling the effects of a recession by the second quarter of 2024. Singh advises Americans to educate themselves about saving money and investing to prepare for the possible downturn.
The article discusses the current state of the economy and questions whether the "soft landing" explanation and belief in a full recovery are accurate, particularly in light of China's economic struggles and global inflation concerns.
Investors are more focused on the release of new forecasts from the Federal Reserve, which will reveal their views on the prospect of an economic "soft landing" and the rate environment that will accompany it.
Federal Reserve Chair Jerome Powell indicates that while policymakers project a "soft landing" for the US economy, he does not confirm it as a baseline expectation due to external factors beyond their control such as the autoworker strike, government shutdown, and higher borrowing costs.
The Federal Reserve has paused raising interest rates and projects that the US will not experience a recession until at least 2027, citing improvement in the economy and a "very smooth landing," though there are still potential risks such as surging oil prices, an auto worker strike, and the threat of a government shutdown.
The Federal Reserve left interest rates unchanged while revising its forecasts for economic growth, unemployment, and inflation, indicating a "higher for longer" stance on interest rates and potentially only one more rate hike this year. The Fed aims to achieve a soft landing for the economy and believes it can withstand higher rates, but external complications such as rising oil prices and an auto strike could influence future decisions.
The U.S. economy is experiencing a higher share of working-age people in the workforce than ever before, and despite some inflationary concerns, the country is not at risk of a recession, according to economist Betsey Stevenson.